Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of GLP-1 receptor agonist delivered through the BioJet™ oral biotherapeutic delivery platform in a porcine model
This preclinical study evaluated the bioavailability of semaglutide following needleless injection in the small intestine using the BioJet platform.
The BioJet™ systemic oral delivery platform (previously called the Oral Biotherapeutic Delivery system, or OBDS) is an ingestible drug-device combination developed to prevent drug degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract and increase drug bioavailability via needleless jet injection in the proximal small intestine following oral administration.
Glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists stimulate insulin secretion and suppress glucagon release. Semaglutide is a GLP-1 agonist currently used to treat type 2 diabetes and for weight management via subcutaneous injection or taken orally. Needle injection is associated with a 42% higher discontinuation rate versus those starting oral therapy.1 However, oral administration of protein/peptide therapeutics has proven difficult due to the harsh conditions of the upper gastrointestinal tract and poor absorption rates in the small intestine. The currently available technology for oral delivery of semaglutide provides approximately 0.4 – 1% bioavailability when delivered in tablet form.2
In this study, we evaluated the ability of the BioJet device to deliver a small-peptide therapeutic via needleless injection into the submucosal space of the small intestine in a swine model by measuring systemic exposure to semaglutide after activation of the device.
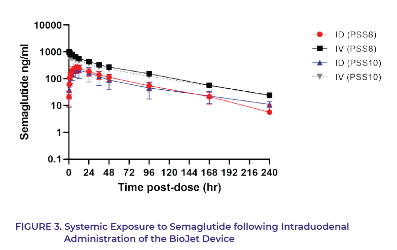
What did we find?
Demonstrated an average bioavailability of 37% ± 15% (CV: 40%), ranging from 19% to 60%.3
All dosed animals showed detectable drug levels up to ten days post-dosing.3
A second study showed similar results with an average oral bioavailability of 37%, demonstrating repeatability of the results.3
The BioJet platform could provide an alternative for the oral administration of large molecules and may improve patient compliance vs. needle-based administration.3
Poster presented at the American Diabetes Association 83rd Scientific Sessions, June 23-26, 2023
Related Publications
REFERENCES
- Spain CV, Wright JJ, Hahn RM, Wivel A, Martin AA. Self-reported Barriers to Adherence and Persistence to Treatment With Injectable Medications for Type 2 Diabetes. Clin Ther. 2016;38(7):1653-1664.e1. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.05.009
- Novo Nordisk A/S. Rybelsus (oral semaglutide) [package insert]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/213051s006lbl.pdf. Revised January 2023. Accessed May 31, 2023. - Lee SN, Stork C, Valenzuela R, et al. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist delivered through the BioJet™ oral biotherapeutic delivery platform in a porcine model. Poster presented at: American Diabetes Association 83rd Scientific Sessions, June 23-26, 2023, San Diego, California.